
![[Tri-Rail Logo]](/gfx/r/trirail4.gif)

![[Tri-Rail Logo]](/gfx/r/trirail4.gif)
Click for full-size graphics ...
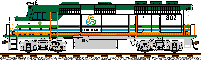 Tri-Rail #802 |
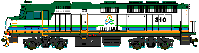 Tri-Rail #810 |
Tri-Rail was authorized in 1989 by the Florida Legislature. Service was started by the Florida Dept. of Transportation at a cost of $75 million, as an alternative to Interstate I-95 during a five-year construction phase in the three highest-populated counties in the state. Services were originally the responsibility of the Tri-County Commuter Rail Authority. Since 2003, the South Florida Regional Transportation Authority (SFRTA), based in Pompano Beach, has operated the system.
In 2009, Tri-Rail transported 4,222,850 riders, compared with 3,862,450 in 2008, 3,392,894 in 2007 and 2,673,947 in 2006. In 2005, Tri-Rail operated 66,628 rail vehicle revenue hours totaling 2,197,808 rail vehicle revenue miles. This accounted for 3,064,074 passenger trips and 85,253,733 passenger miles. Operating expenses averaged $20 million annually.
As of 2020, Tri-Rail's federally-defined service area included over 6 million residents, with roughly 2.7 million in Miami-Dade, 1.9 million in Broward and 1.5 million in Palm Beach counties.
Tri-Rail typically carried 15,000 weekday riders and 4,000 on weekend days [as of 2008] over its 72 mile, 18-station route. The weekday schedule provided for 25 trains each direction running every 20 to 60 minutes. On weekends the frequency was reduced to every 2 hours.
The Tri-Rail right-of-way through Dade, Broward and Palm Beach counties nearly parallels Interstate 95 and is shared with Amtrak passenger trains and CSX freight trains. It is the southern end of the original "Seaboard Airline Railroad" route which was laid with single track. Double-tracking of the system was completed in 2006, except for a segment over the New River in Fort Lauderdale, which was completed in April 2007.
Each trainset normally consisted of four bi-level passenger cars and a diesel-electric locomotive. The trains operate in "Pull South/Push North" mode with the locomotive at the south end of the consist facing Miami. The bi-level car at the north end of the train is a cab car, having controls for the engineer when the train is pushed northbound.
Tri-Rail's maintenance base used four tracks in the former Seaboard Airline Railroad locomotive shop. The facility is located immediately north of the Miami Amtrak station and approximately 12 blocks north of the Tri-Rail/Metrorail Transfer Station.

16 DIESEL-ELECTRIC LOCOMOTIVES
| Numbers | Type/Model | Builder & Year | Power | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 801-805 | F40PHL-2 | Electro-Motive, 1968; Rembuilt by Morrison Knudsen, 1987. | 3,200HP; Shaft-driven alt. HEP | Rebuilt from Conrail GP-40-2. Being rebuilt 1995/96. |
| 807-809 | F40PHC-2C | Morrison Knudsen, 1992 | 3,000HP; Caterpillar V-12 HEP | -- |
| 810-811 | F40PHR | Electro-Motive, 1981 | 3,000HP; 800KW alt. HEP | Purchased from Amtrak Nov '96. Former Amtrak 363 & 379. |
| 812-817 | GP49 | Electro-Motive, 1980 | 2,400HP; HEP | Former Norfolk Southern. |
| Numbers | Type/Model | Builder & Year | Seats | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 501-506 | Passenger Coach w/Cab Control | Urban Transit Development Corp (Lavellin), 1987 | 154 | Luggage rack, bicycle rack & space for 2 wheelchairs. |
| 507-511 | Passenger Coach w/Cab Control | Bombardier, 1996 | 126 - 135 | Full-width cab. Handicapped restroom, large luggage rack, bicycle rack & space for 4 wheelchairs. |
| 1001-1012 | Passenger Coach | Urban Transit Development Corp (Lavellin), 1987 | 155 | Restroom, luggage rack & bicycle rack. |
| 1013-1015 | Passenger Coach | Bombardier, 1990 | 157 | Restroom, luggage rack & space for 2 wheelchairs. |
Each Bi-Level car features full headroom on each level, air-conditioning, drinking fountain, restroom, and two-sets of double-wide doors. Tri-Rail GIF image by Media by McCann. Equipment roster courtesy of the Tri-Rail Operations Department.
About color schemes: The colors on this page show Tri-Rail's green, blue and orange on white.